Hexokinase Conformational Change
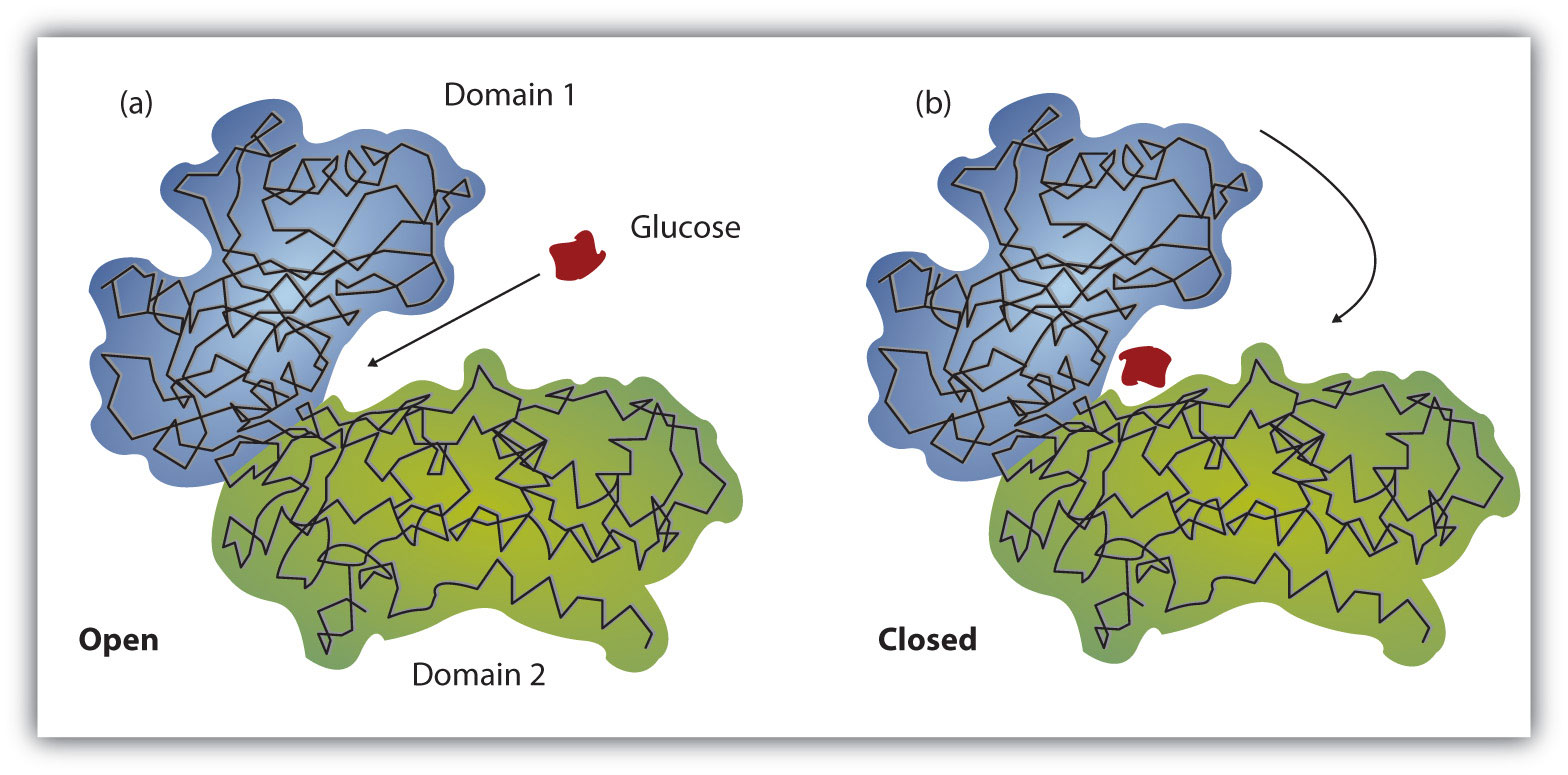
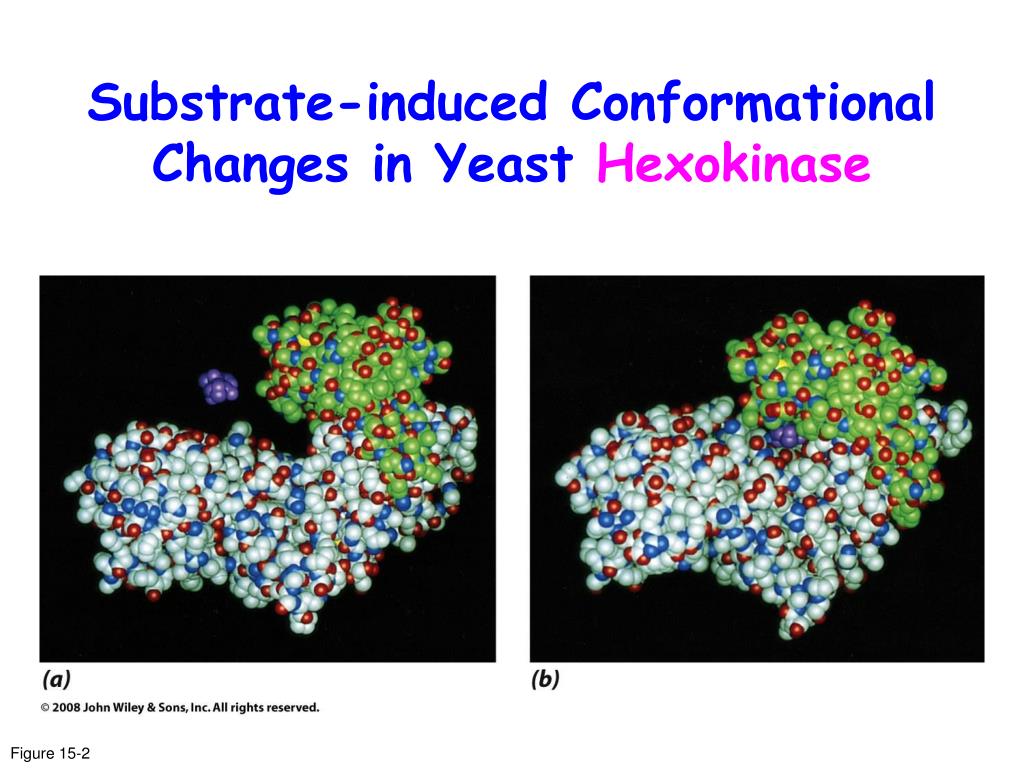
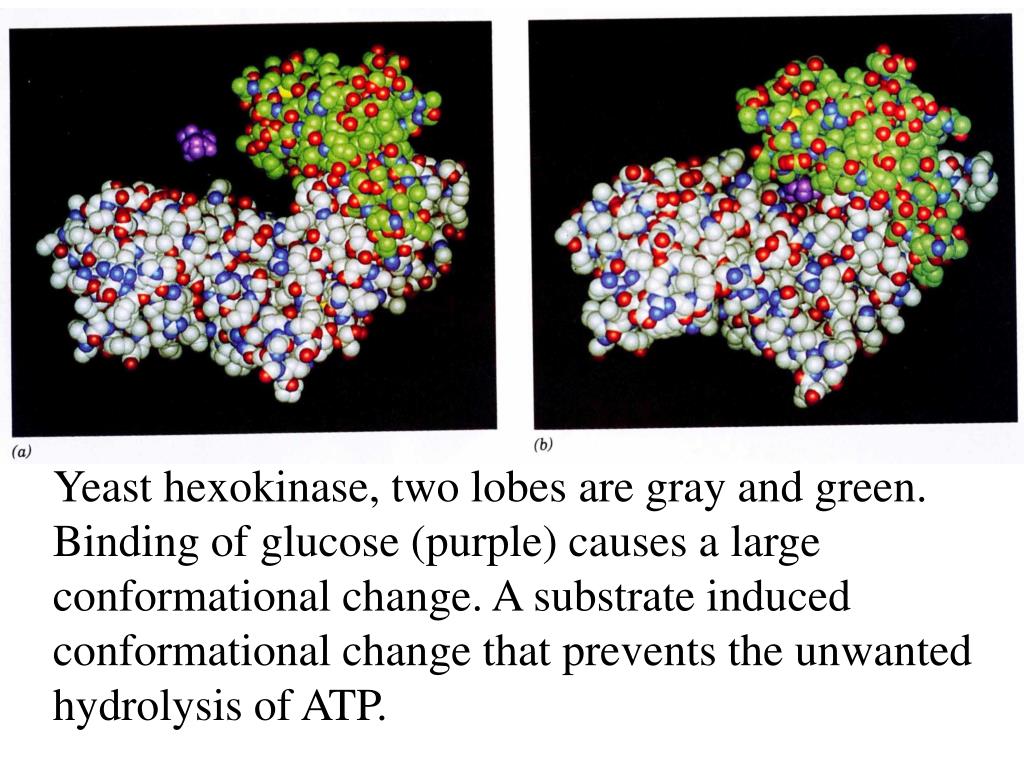
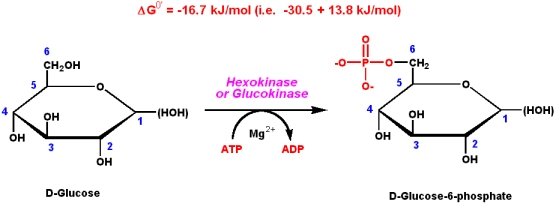
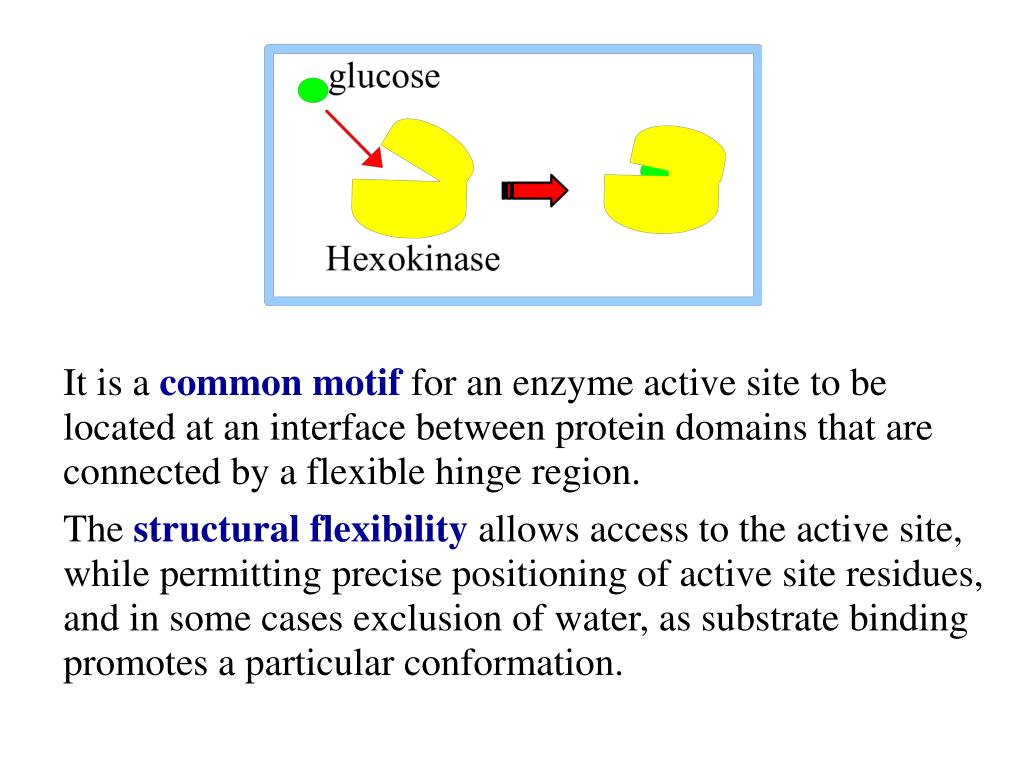
Hexokinase undergoes an induced fit conformational change when glucose binds.
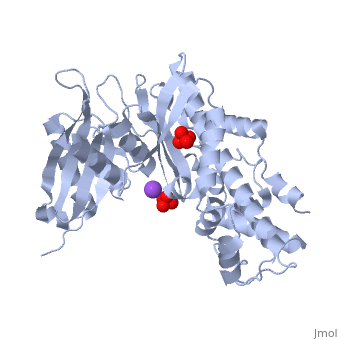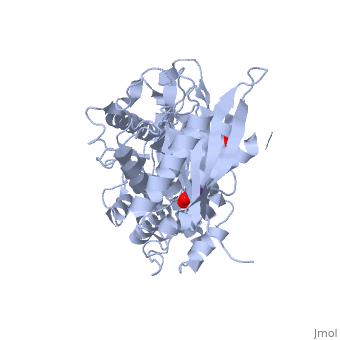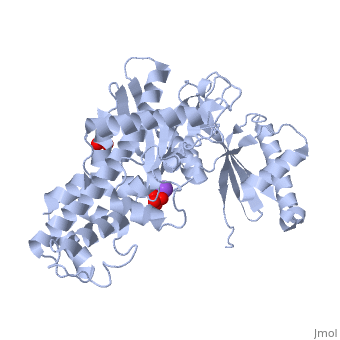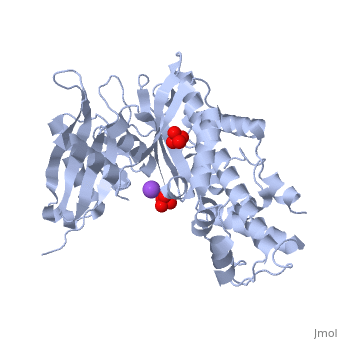
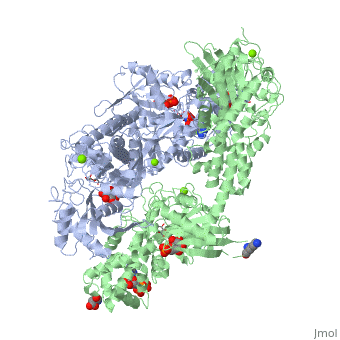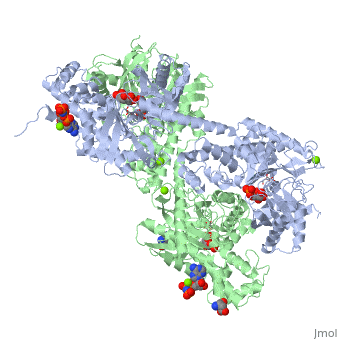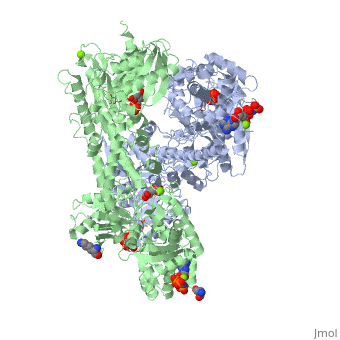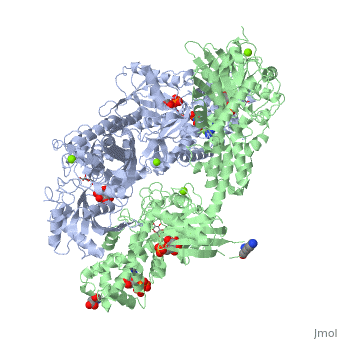
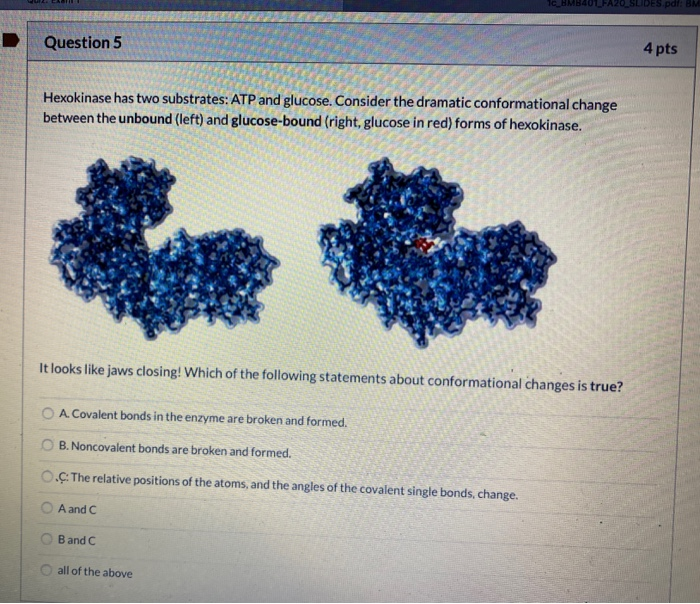
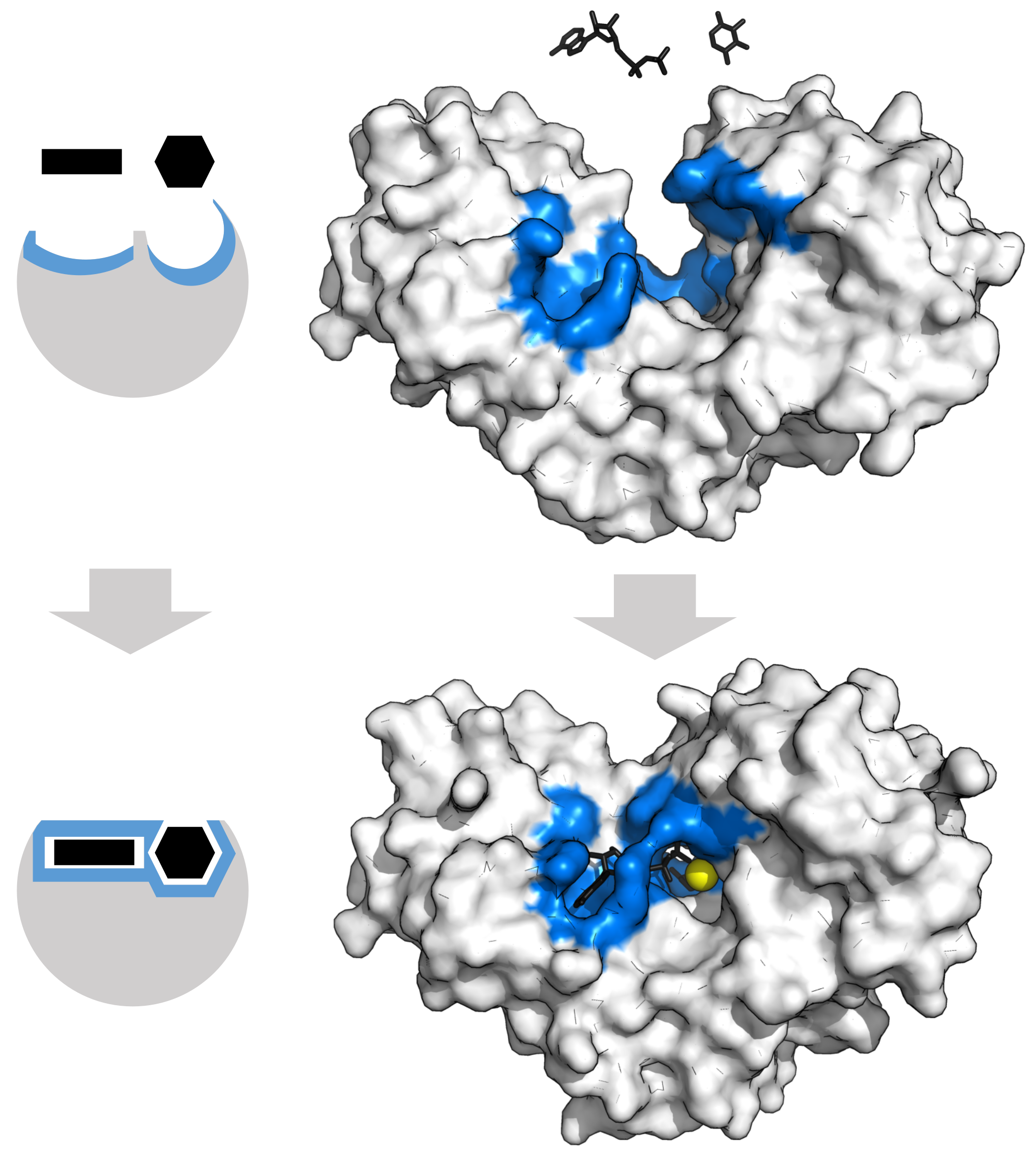
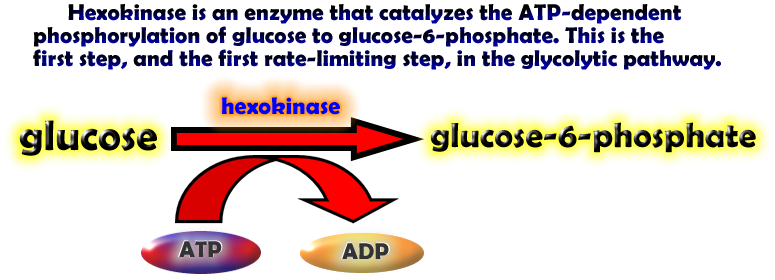
Hexokinase conformational change. Fig 6 structure of hexokinase fig 7 active site of glucokinase hexokinase. Fig 4 lock and key model. Transient kinetic analysis biochemistry. The a isozyme of yeast hexokinase atp d hexose 6 phosphotransferase ec 2 7 1 1 crystallized as a complex with glucose has a conformation that is dramatically different from the conformation of the b isozyme crystallized in the absence of glucose.
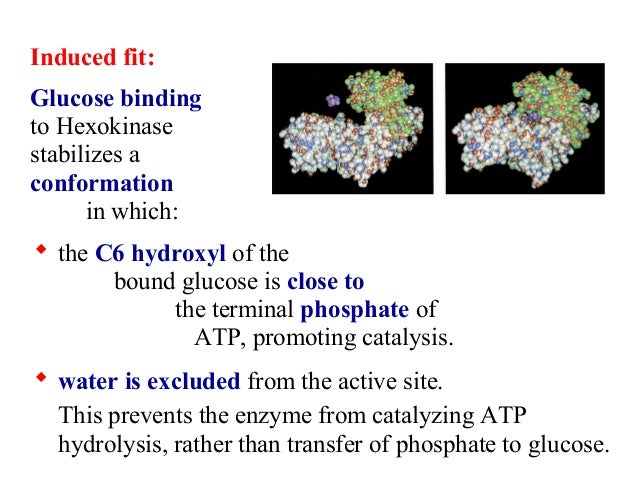
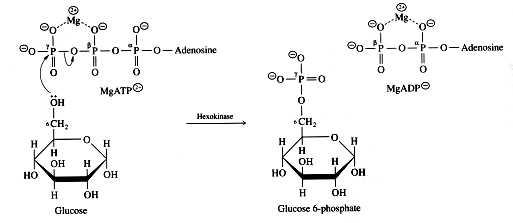
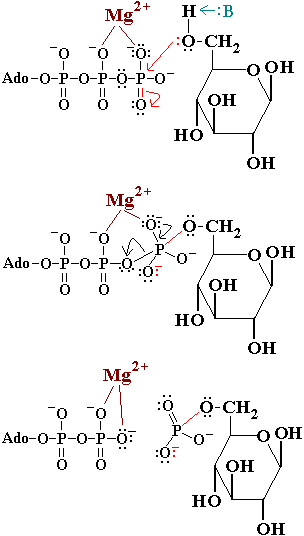
Hexokinase has two conformational states. Bennett huber 1985 and large scale conformational changes e g. Mgatp 2 hexose hexose 6 p mgadp is the prototypical enzyme exhibiting an induced conformational rearrangement in and surrounding the active site. This conformational change prevents the hydrolysis of atp and is allosterically inhibited by physiological concentrations of glucose 6 phosphate the product.
What would happen if hexokinase did not undergo a significant conformational change via induced fit when binding glucose and atp. Meanwhile the first 12 amino acids of the highly hydrophobic n terminal serve to bind the enzyme to the mitochondria while the first 18 amino acids contribute to the enzyme s stability. Bennett ws jr steitz ta. The binding synergism of glucose and gluc 6 p probably arises out of the mutual stabilization of a common glucose bound conformation of hexokinase l.
The glucose induced conformational change in hexokinase bennett steitz 1978 flexible to rigid transitions e g. Conformational changes in the n terminal domain in response to glucose phosphate and or gluc 6 p may influence the binding of atp to the c terminal domain. A change in the conformation of an enzyme in response to substrate binding that renders the enzyme catalytically active. The open state occurs prior to glucose binding.
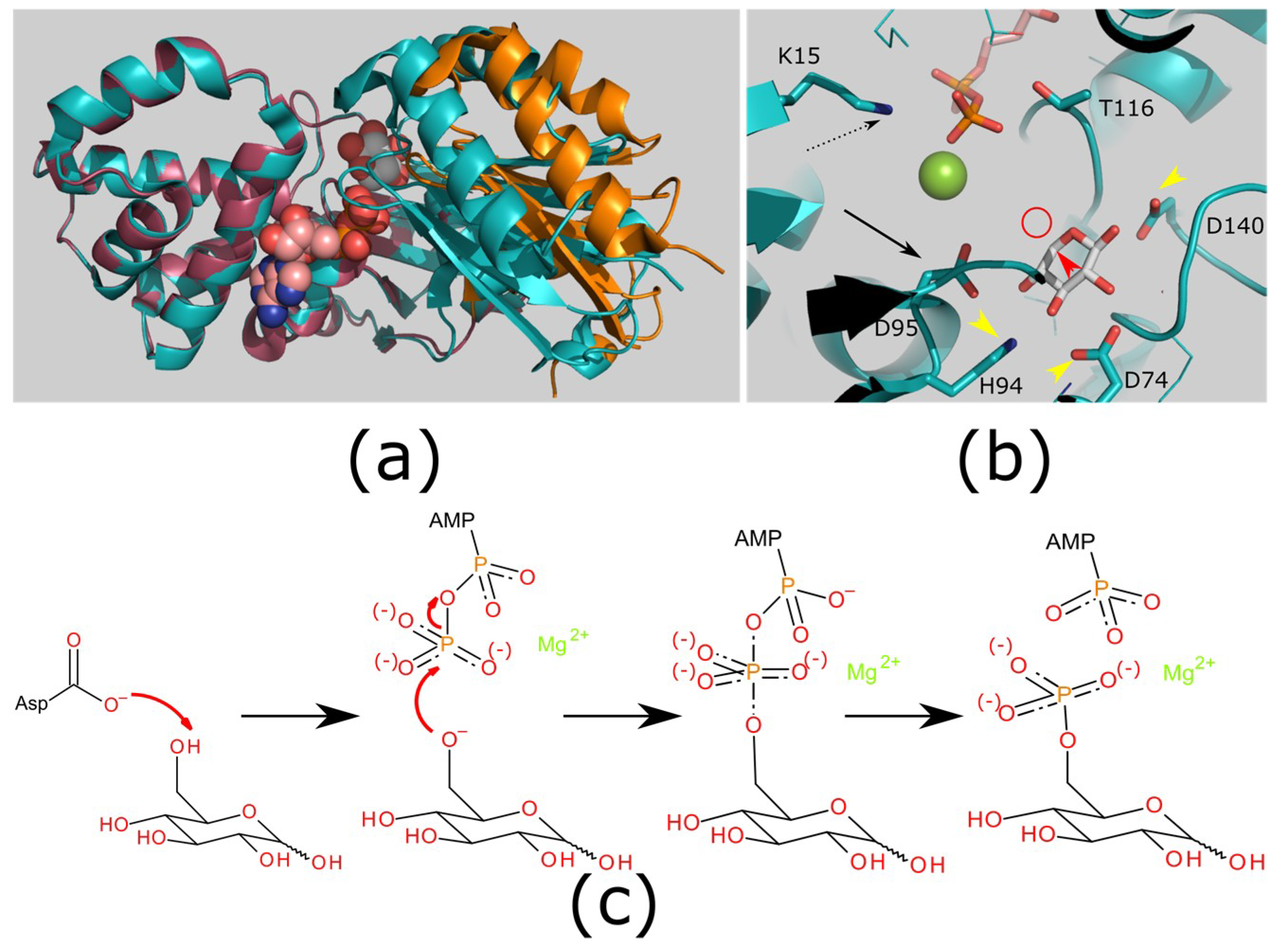
Fig 3 mechanism of phosphorylation catalyzed by hexokinase. Glucose induced conformational change in yeast hexokinase. The tran sition from a straight to a bent conformation of the central connecting helix in calmodulin. However instead allowed access of water into its active site.
Affiliation 1 biochemical. Glucose induced conformational changes in glucokinase mediate allosteric regulation. Fig 5 induced fit model. The a isozyme of yeast hexokinase atp d hexose 6 phosphotransferase ec 2 7 1 1 crystallized as a complex with glucose has a conformation that is dramatically different from the conformation of the b isozyme crystallized in the absence of glucose.
Authors vladi v heredia 1 jim thomson david nettleton shaoxian sun. Comparison of the high resolution structures shows that one lobe of the molecule is rotated by 12 degrees relative to the other lobe resulting in movements of as much as 8 a in the polypeptide backbone and closing the cleft between the lobes. That the enzyme exhibits an activatable intrinsic atpase activity reaction.